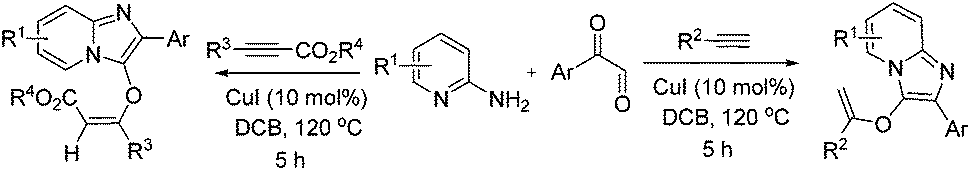Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis since r 1 r 2 r 3 can be combinations of differing groups which can be varied in order to provide a.
Formation of vinyl ethers.
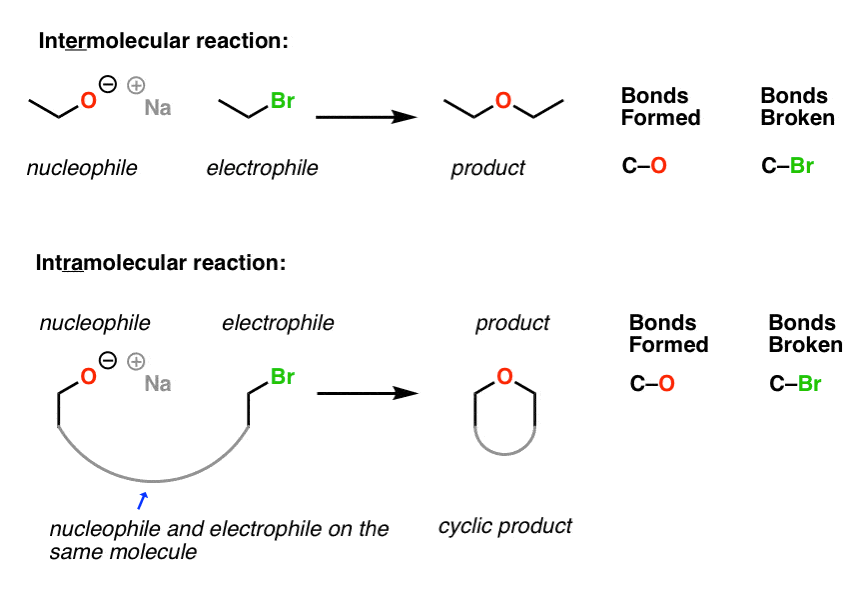
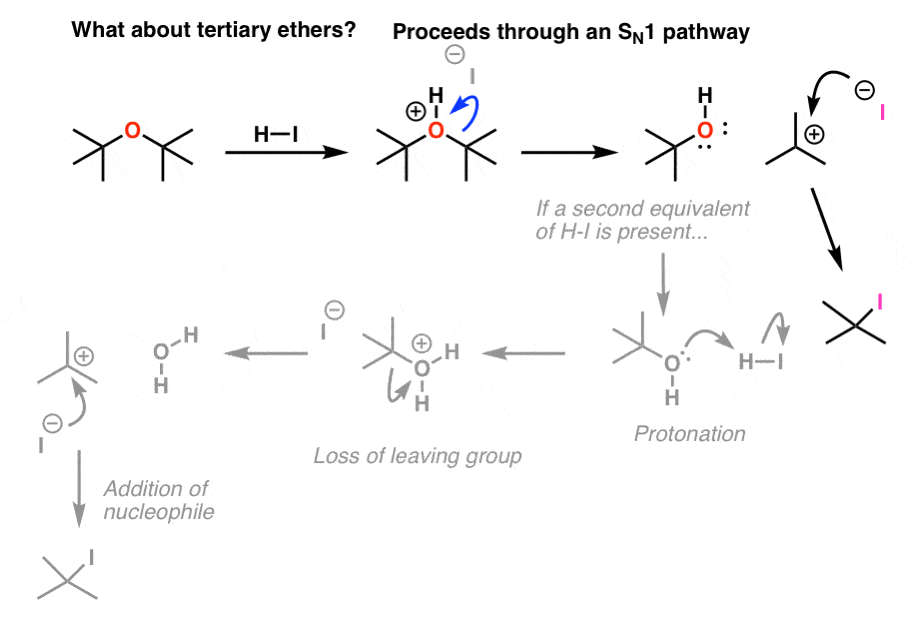
3 1 halide and pseudohalide leaving groups.
Palladium ii complexes catalyze the formation of enamides via the formal cross coupling reaction between nitrogen nucleophiles and vinyl ethers.
A stereospecific and stereoselective copper promoted coupling of vinyl pinacol boronate esters and alcohols allows the synthesis of enol ethers in very good yields is compatible with various functional groups and occurs at room temperature.
2 3 acetylenic ether substrates.
Silyl ether formation may be avoided.
Molecular structure is the primary factor relating to a material s potential for hazardous peroxide formation.
In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent.
The general structure is r 2 c cr or where r h alkyl or aryl a common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers with the formula roch ch 2 important enol ethers include the reagent 3 4 dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether.
Glycol ethers decalin and 2 propanol are shown in group b of the previous section.
Silyl enol ethers have been prepared by reaction of carbonyl compounds with hydrosilanes in the presence of palladium salts rhodium complexes and nickel salts.
It is also important that r is a good radical leaving group.
3 2 alkoxide and silyloxide leaving groups.
4 olefination of carbonyl substrates.
2 modification of ethers.
These vinyl transfer reactions proceed in good yields with amide carbamate and sulfonamide nucleophiles and the optimal catalyst is dpp pd ococf3 2 dpp 4 7 diphenyl 1 10 phenanthroline.
2 2 allyl ether substrates.
Sakurai 177 has found that dicobalt octacarbonyl is an excellent catalyst for the reaction equation 67 and that the side reactions occurring through the use of the catalysts mentioned above e g.
Ethyl ether is an excellent solvent for extractions and for a wide variety of chemical reactions.
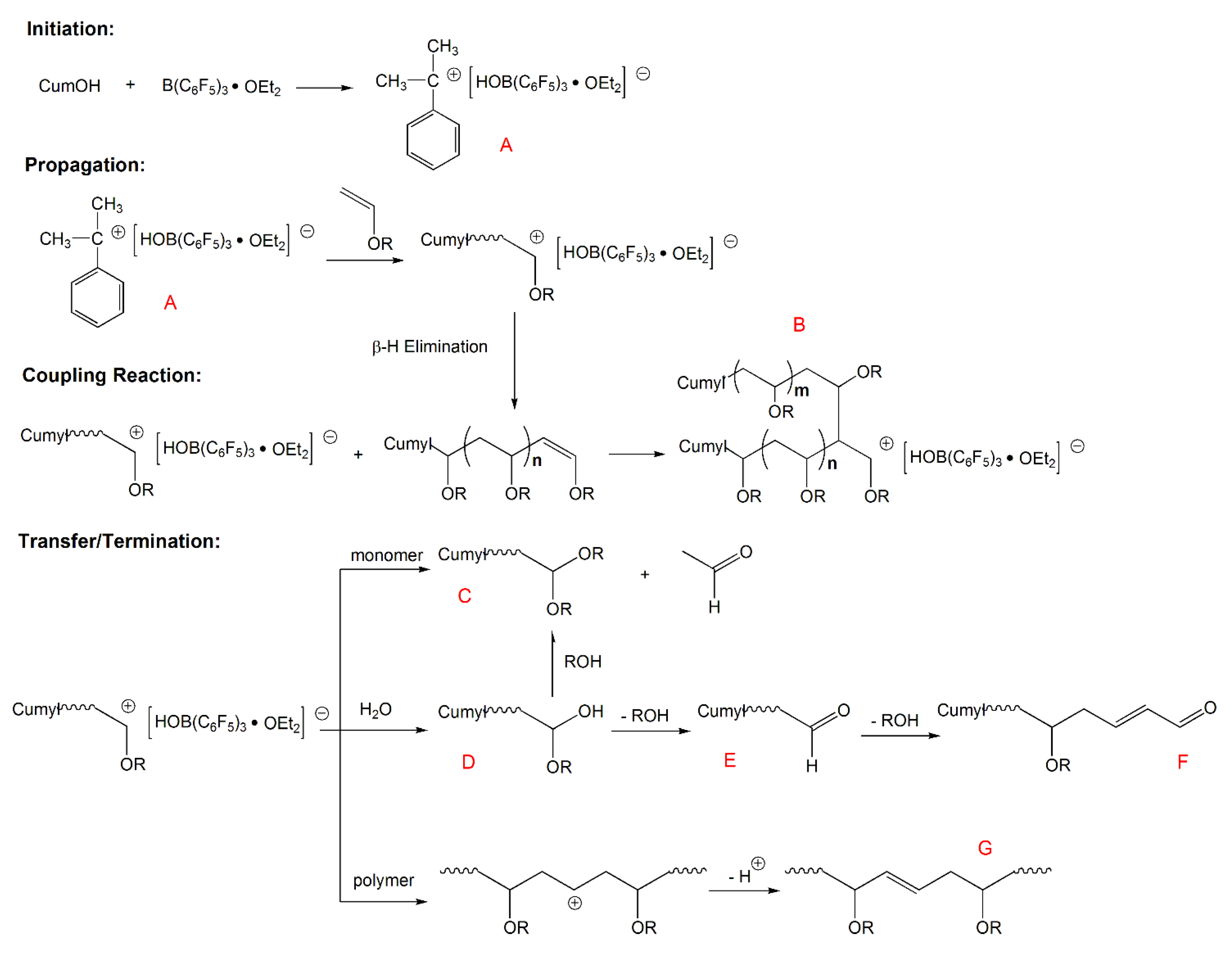
Vinyl ethers 1 x ch 2 a o can be very effective addition fragmentation chain transfer agents.
The general structure is r 1 r 2 r 3 si o r 4 where r 4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group.
8 21 227 228 the mechanism for chain transfer is shown in scheme 9 for the case of α benzyloxystyrene 15 the driving force for fragmentation is provided by formation of a strong carbonyl double bond.
Cupric acetate is the copper source and triethylamine buffer is used to prevent protodeboration.
It is also used as a volatile starting fluid for diesel engines and gasoline engines in cold weather.
Methyl t butyl ether mtbe is a gasoline additive that boosts the octane number and reduces the amount of nitrogen oxide pollutants.
2 1 vinyl ether substrates.